|
www.stomach-reflux.com Treat Acid Reflux Today |

|
|




Diagnosis of GERD and stomach reflux acid disease
How to diagnose heartburn, acid reflux and GERD
When patients present with typical symptoms and no complications, the diagnosis of GERD is usually straightforward. Doctors can usually diagnose GERD if the patient finds relief from persistent heartburn and acid regurgitation after taking antacids for short periods of time. Some patients have GERD that doesn't respond to treatment. Or they may have other associated symptoms, such as weight loss, difficulty swallowing, complications such as sign of bleeding or black stools. In this case , the following tests including endoscopy may be needed:
Upper endoscopy (GI) is a nonsurgical procedure that helps the physician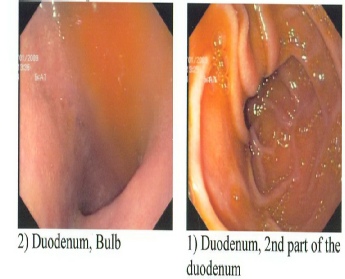 (normally a gastroenterologist ) to examine patient’s digestive tract using a tiny flexible viewing tube attached to a camera and light . It is widely used in GERD / acid reflux for identifying and grading severe esophagitis, monitoring patients with Barrett's esophagus, or when other complications of GERD are suspected. Upper endoscopy is also used as part of various surgical techniques
(normally a gastroenterologist ) to examine patient’s digestive tract using a tiny flexible viewing tube attached to a camera and light . It is widely used in GERD / acid reflux for identifying and grading severe esophagitis, monitoring patients with Barrett's esophagus, or when other complications of GERD are suspected. Upper endoscopy is also used as part of various surgical techniques
An endoscope is a thin flexible plastic tube containing a tiny camera, when it is inserted through the mouth, the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and upper duodenum can be visually viewed on TV monitor for any abnormalities or growths. In this procedure the camera enables the doctor to see the surface of the esophagus and to look for abnormalities, including hiatal hernia and damage to the mucous lining. The physician may perform a biopsy (the removal and microscopic examination of small tissue sections). The biopsy can detect tissue injury indicating GERD. It may also be used to detect cancer or other conditions or viral infections (such as herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus). Such infections are more likely to occur in people with impaired immune systems. Details on next page
Barium Swallow radiograph test for GER
A barium swallow radiograph (x-ray) is a diagnostic test that may be used to diagnose GERD and determine the cause of painful swallowing, difficulty with swallowing, abdominal pain, bloodstained vomit, or unexplained weight loss. This test is used for identifying structural damage to the esophagus including stricture, active ulcer craters, hiatal hernia, erosion, or other abnormalities that may indicate acid reflux disease. Barium sulfate is a metallic compound that shows up on X-rays . When taking the test, the patient drinks a solution containing barium, and then x-rays of the digestive tract are taken.
Manometry is a technique that may be used for acid reflux to measure the function of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES ) and the muscles of the esophagus . During the manometry test, a tube is passed through the nose, along the back of the throat, down the esophagus and into the stomach. As the muscular action of the esophagus exerts pressure on the tube in various locations, a computer connected to the tube measures this pressure. This test is used to identify problems with movement and pressure in the esophagus that may lead to problems like heartburn and GERD. This test will tell your doctor if your esophagus is able to move food to your stomach normally. It helps to understand the swallowing and digestive processes.
The manometry test may be given to patients who have the following symptoms:
Chest pain
Heartburn or reflux.
Difficulty swallowing.
| Stomach Overview |
| What is reflux acid |